Uncollateralization vs. Overcollateralization in DeFi – The Difference is Striking
Learn the different options of loans in the DeFi ecosystem

It goes without saying that there are many types of loans by lending protocols in DeFi and the current dominant version is over-collateralized loans. However, uncollateralized lending is beginning to appear where lending protocols are offering loans without asking for collateral deposit from you.
Now, let’s examine the differences between these two options.
Overcollateralized Loan Takes More From You Than What You Receive
Overcollateralization simply means you have to give the lender more than what you get out from them. So, you need to provide collateral where its value is more than the value that you are borrowing from them.
If you wish to borrow 1 BTC, you have to put in 1.3 BTC as collateral, for example. It sounds ironic doesn’t it because the very reason you apply for a loan is you need money and yet you are asked to deposit more “money” than the amount you intend to borrow.
You’re forced to swallow this bitter irony pill thanks to the volatility of cryptocurrency prices. It simply protects the lender, not you.
Due to this very nature, overcollateralized loan is not for everybody. It mainly serves those with existing digital assets who aren’t ready to liquidate them. Lending protocols that offer these kinds of loans are Aave, Compound and many more. Think of them like pawn shops. Anyone, regardless if you’re an institution or individual, can borrow from them as long as you deposit your collateral.
Over-collateralized loans aren’t new in this world. In fact, it’s a common practice in traditional finance. Jonathan Tompkins wrote an intriguing article denying the existence of under-collateralized loans. His argument is that your mortgage loan is over-collateralized because your home is the collateral and your bank only lends you below or close to the market value of your house. If you default, they take your home and resell them at market value thus covering their loss.
However, Tompkins’ take on the meaning of collateral seems twisted because he takes into account the borrower’s income and ability to repay as a form of collateral. By definition, a collateral is an asset – usually physical – that is deposited as a form of guarantee that a borrower could repay a loan. So you see, there’s some sort of asset exchange between the borrower and the lender.
Uncollateralized Loan Needs Nothing From You Except Your Credit History or Score
An uncollateralized loan, on the other hand, has no exchange of assets. One simply gets a loan without having to pledge any assets to the lender as security. As long as the borrower is creditworthy, they should be able to receive an uncollateralized loan within their ability to repay them. That is usually decided by the borrower’s credit history or credit score. As examples, the unified credit scoring system in the US is called FICO score while in Singapore, it is managed by Credit Bureau Singapore.
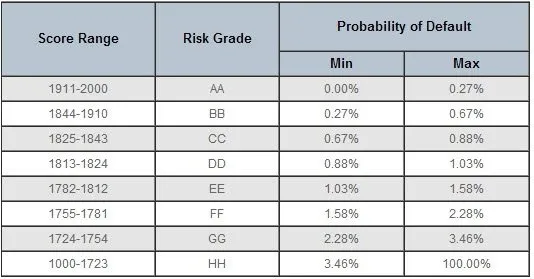
To ensure you can safely repay a loan, lender checks your financial and borrowing background to see how well are you as a paymaster and how much expenses you’re bearing against your income. Say, currently you have no other debts and your monthly expenses are much lower than the salary you bring in every month, this means you have a high chance of paying back the money the lender would loan you. Another positive indicator that you’re creditworthy is that you constantly repay your loan installments or settle your bills on time.
If you are heavily burdened with other loans or your credit history indicates that you sometimes misses loan payments, this is a sign that you may not be such as great paymaster.
Generally, there are three types of uncollateralized borrowing in DeFi.
- Uncollateralized borrowing by institutions
- Uncollateralized borrowing by individuals via crypto credit card
- Flash loans
Uncollateralized Borrowing By Institutions
Some of these players are TrueFi and Atlendis, both offering loans to institutions only. This means you must be a company or an organization to receive their loans. Each applicant will have to go through a vetting (aka scoring) process and TrueFi does it via a DAO on Snapshot.
Uncollateralized Borrowing via Crypto Credit Card
We, at CryptCard, offer uncollateralized loans to individuals in the form of crypto credit cards without collateral. The crypto cards enable you to transact in cryptocurrency and the beauty of it is it eliminates the need to pay gas in every transaction. Any individual could apply for the card and it involves a credit scoring process. You can conveniently use your crypto wallet as your credit card when transacting on GameFi, DeFi, DEX, NFT sites, and dapps that support the card.
Flash Loans
As the name implies, this type of uncollateralized lending works by having a lender lending out to a borrower but the caveat is the borrower has to repay “in a flash”. This flash means the entire process must happen within a single blockchain transaction inside the loan’s smart contract. There’s no credit score required. This speedy behavior makes this sort of lending practice safe for the lender because the smart contract will not execute if the borrower cannot repay the loan in the first place. If you wish to learn the underlying mechanics of a flash loan, here’s a step-by-step guide. The speedy architecture of this lending method gives it a very niche market within DeFi scope as it’s almost only used for token trading.
Overcollateralized Interest Rate Follows Supply and Demand
The interest rate set in overcollateralized loans in DeFi usually follows the demand and supply of liquidity. For instance, on Aave, the borrowing interest rates are determined based on the utilization of tokens in the pool. This means if fewer people are borrowing from the pool, the rate is set low to incentivize people to borrow. And the opposite is true, if assets are being depleted by borrowers, the rate is set higher. This encourages lenders to add more assets into the pool and motivates borrowers to return the assets due to the high interest.
Uncollateralized Interest Rate is Determined By How Creditworthy You Are
An uncollateralized loan typically requires a higher interest rate because the lender is taking more risk by not demanding any collateral from you. This clearly reflects the “high risk, high return” paradigm. This is why uncollateralized lending is categorized as unsecured lending in traditional finance.
However, the rate depends on how creditworthy you are. If you’re religious in managing your finance, you could get a lower interest rate because you are deemed a low-risk borrower. This is fair to the borrower and the lender.
In the spirit of fairness, CryptCard offers credit cards with interest rates according to your creditworthiness. This rate is set and doesn’t fluctuate which makes it easier to keep track of.
Both Overcollateralized and Uncollateralized Loan Amount Can Be Big or Small
Although it depends on the purpose of the loan, the amount for both types of loans can vary tremendously. There’s no clear distinction between the two.
Take TrueFi for example. They offer uncollateralized loans to businesses ranging from $10,000 to 10 million dollars. For the overcollateralized option, it depends on the value of the collateral you can offer. This applies to lending protocols such as Aave or Compound.
CryptCard offers uncollateralized credit limits for its cards from as little as $1,000 to $30,000 or more. It depends on your credit history.
